Getting Started with C++
Every programming language has some boilerplate material that we use to start a programming project. Mostly it is code to describe where the program should start and what additional libraries should be used to augment the programming language itself. Thus we have, in every language, this smallest program that we can write. We will ignore some of the explanation as to exactly what these minimal programs are doing until later. It is sufficient for now that we treat this as boilerplate code that forms the foundation of our programs. We can then expand upon these boilerplate programs as we explore the various features of the language.
/******************************************************************************
* Simple first program.
*
* Copyright © 2020 Richard Lesh. All rights reserved.
*****************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
cout << "Hello, world!" << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
This approach to introducing a programming language by writing a simple program that outputs one phrase, typically "Hello, world!" was first seen in Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie's book "The C Programming Language" in the 1970s.
Language Execution Models
In order to get our programs as they are written in our favorite language to run on a computer, it is necessary to convert from the English-like text of our source code to something that the computer CPU can understand. Depending on the language, this either involves a compilation or interpretation phase. Some modern languages require both phases.
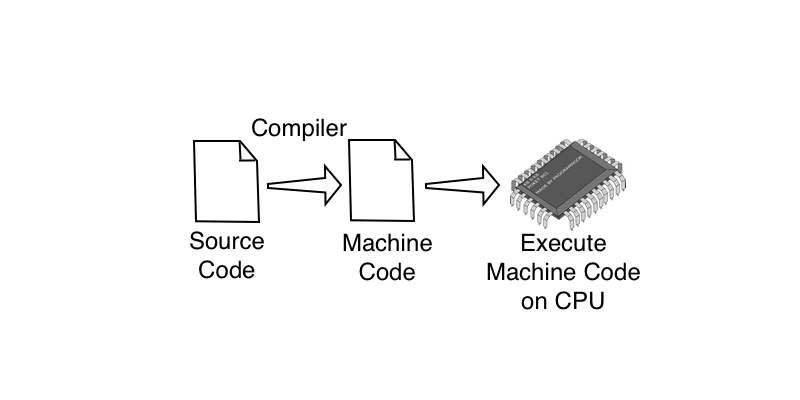
Compilation involves taking our source code and then translating it into another language, typically the language of the CPU known as machine language. Compilation is typically performed by a program called a compiler and it is a required step when writing in a compiled language. Once our program has been compiled into machine code, we can then run it directly on the CPU. Languages such as C, C++, Objective C, Swift, FORTRAN and Cobol are all compiled languages. These languages are typically used in the development of operating systems and commercially distributed code.
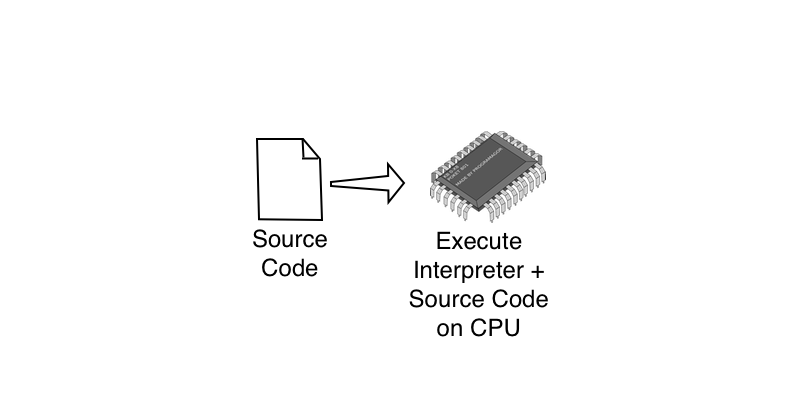
Interpretation involves taking our source code and then line by line decomposing the source into steps that are immediately carried out by the CPU. Interpreted languages require a program called an interpreter to perform this function. There is no compilation phase, we just get to the business of running our program straight from the source code each time we want it to run. Compared to compiled languages, it can often be easier to develop and debug interpreted programs. Interpreted languages, often called scripting languages, include JavaScript, Python and Ruby.
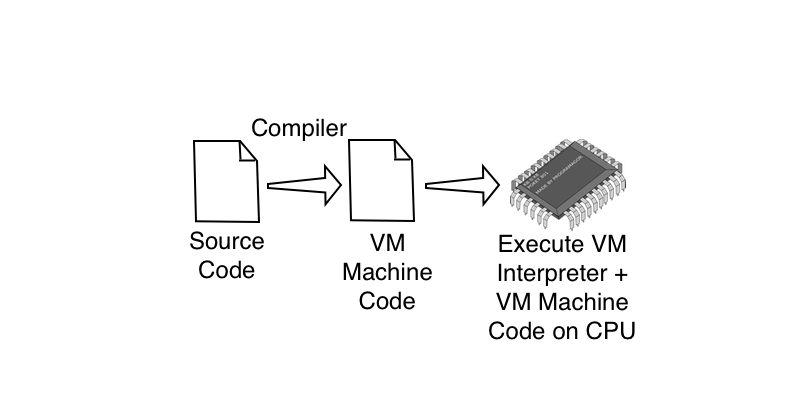
Some languages, most notable are Java and JavaScript, use both approaches. In the case of Java, the source code is compiled to the machine code for a fictional CPU known as the virtual machine (VM). Because your CPU doesn't typically use the same instruction set as the virtual machine, the compiled program must then be interpreted by a program that in essence pretends to be the virtual machine. So languages that use a VM have both a compiled and an interpreted phase. Notable VM languages are Java and C#.
Tool Setup
Because C++ uses the Compiled Language Execution Model we need to have the following software tools available to us: programming text editor to create/edit our source files, compiler and linker to translate our source files into a native executable program, and a command-line console to launch the program and handle the input and output from our program.
Command-Line Console
The Command-Line Console is used to invoke the JavaScript interpreter and is also used by the programs we write for text input and output. Linux, Mac OS X and Windows all come with a Command-Line Console program though many are not accustomed to using it.
- In Linux the Command-Line Console is immediately available if booting in text mode. If booting in the Gnome graphical interface, it is typically available under the Application Menu -> Accessories -> Terminal.
- In Mac OS X the Command-Line Console is found in the Applications folder -> Utilities -> Terminal.
- On the Raspberry Pi the Command-Line Console is immediately available if booting in text mode. If booting in the Gnome graphical interface, it is available under the Application Menu -> Accessories -> Terminal.
- In Windows the Command-Line Console is found under the Start Menu -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Command Prompt. On Windows there are many more functional terminal emulator programs than the built-in one available such [[ConsoleZ]].
On this site we will use the terms console, terminal and command-line prompt interchangeably. Illustrations of terminal command sequences will be presented in a box with a black background. User input will appear in white while the command prompts ($) and program output will appear in green.
$ user input program output
Programming Text Editor
Programming Text Editors can be as simple as a plain text editor or as complicated as a text editor built-in to an Integrated Development Environment (IDE). For our purposes a middle-of-the-road programming editor will suffice. These types of text editors offer some niceties beyond the basic ability to edit text files. The most common of these programming oriented features is syntax highlighting which colors the parts of the programming text to indicate its role in the programming language's syntax. Other features include auto-completion, auto-balancing of brackets and auto-indenting of source code.
Programming Text Editors are not the same types of programs as Word Processing software. Word Processing software is designed to format and layout complex text documents such as manuals, brochures or flyers. The documents that they create are stored in special word processing formats that are not compatible with our programming tools. Programming Text Editors not only have features aimed at helping write programs, but more importantly they save the source files in a plain text format ([[ASCII]] or [[UTF-8]]) required by our programming tools.
While bare-bones text editors that come with your OS like TextEdit (Mac OS X), LeafEdit (Raspbian) or Notepad (Windows) will work to edit our source code files, you will be more productive using a programming text editor. Based on your operating system you might try some of the programming text editors listed below.
- Linux: [[GEdit]] (Free), [[Geany]] (Free), [[Komodo Edit]] (Free), [[Sublime Text]] (Free), [[UltraEdit]], [[Visual Studio Code]] (Free)
- Mac OS X: [[GEdit]] (Free), [[Geany]] (Free), [[BBEdit]], [[Komodo Edit]] (Free), [[Sublime Text]] (Free), [[TextMate 2]], [[UltraEdit]], [[Visual Studio Code]] (Free)
- Raspberry Pi: [[GEdit]] (Free), [[Geany]] (Free), [[Visual Studio Code]] (Free)
- Windows: [[GEdit]] (Free), [[Geany]] (Free) [[Komodo Edit]] (Free), [[Notepad++]] (Free), [[Sublime Text]] (Free), [[UltraEdit]], [[Visual Studio Code]] (Free)
Most Linux distributions based on the Gnome desktop will come with GEdit already installed. Some, however, like the distribution for the Raspberry Pi do not. If your distribution does not have GEdit installed it is easy to install from the command-line terminal using apt.
$ sudo apt install gedit
Raspberry Pi OS comes with Geany already installed. If your Linux distribution does not have Geany installed it is easy to install from the command-line terminal using apt.
$ sudo apt install geany
Visual Studio Code can be installed on Linux distributions including Raspberry Pi OS from the command-line terminal using apt.
$ sudo apt install code
Compiler and Linker
To see if your system already has the [[GNU C++ Compiler]] tool chain installed, use the terminal to print the version of your installed compiler.
On MacOS X you will see version information for the [[Clang C++ Compiler]] instead.
If you don't see the G++ version information illustrated above, then you do not have the compiler installed.
To install the Gnu C++ compiler tools on a Debian-based Linux distribution like Ubuntu or Linux Mint, use terminal to run apt.
To install the Clang C++ compiler tools on MacOS X, you must download and install the XCode development tools from the AppStore. You then need to launch XCode once. Answer yes when it asks if you wish to have the command-line tools installed.
The Raspbian Wheezy distribution for Raspberry Pi comes with the Gnu C++ compiler already installed. If it does not, use the Linux installation instructions above.
To install the Gnu C++ compiler on Windows, the easiest way is to install the [[Cygwin]] Unix tools. Cygwin gives Windows users access to a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution. Download the 32-bit or 64-bit version of the Cygwin installer depending on your version of Windows. The installer will step you through a number of setup options, the defaults are good for most cases. When the installer gets to the "Select Packages" screen you want to be sure to select gcc-g++ Gnu Compiler Collection (C++). You can search for it or locate it yourself in the "Devel" category. If it says "Skip" simply click on the word "Skip" to change it to the version you wish to install (typically the latest).
When the installation is complete, elect to have an icon created on your desktop. You will use this Cygwin icon to launch the Cygwin terminal whenever a command-line terminal is required.
References
-
[[C++ Programming Language]], 4th Edition, Bjarne Stroustrup, Addison-Wesley, 2013, ISBN 978-0321563842.
- [[C++ Language Reference]]
- [[cplusplus.com]]
- [[Cprogramming.com]]
 Pure Programmer
Pure Programmer


